Introduction
Gender incongruence (GI) is defined as a strong and persistent discordance between the sex assigned at birth and the gender with which a person identifies [1]. Transgender women (TW) are assigned male at birth but identify as women, while transgender men (TM) are assigned female at birth but identify as men. Individuals whose gender does not fit into the male-female dichotomy are commonly referred to as non-binary (NB). Some transgender and gender diverse (TGD) individuals may seek to align their expression and physical appearance through social, medical (hormonal and/or surgical), or administrative means. Gender dysphoria (GD) refers to the discomfort or distress that individuals may experience when their gender identity differs from their sex assigned at birth. Not all TGD individuals experience GD, and its intensity can vary.
Hormonal and surgical treatments aim to alleviate GD and improve the psychosocial well-being and psychiatric comorbidity of TGD individuals [2,3]. Gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) is an individualized and multidisciplinary treatment that involves reducing endogenous sexual hormone levels to minimize secondary sexual characteristics associated with the sex assigned at birth, while increasing hormone levels according to the desired gender. Both GAHT and gender-affirming surgical treatments can affect the fertility of TGD individuals, most of whom are in puberty or the reproductive period [4,5]. In many countries, gender-affirming surgery has been or still is a requirement for legal recognition of gender change, often resulting in irreversible loss of fertility as a consequence of the transition process [6]. Therefore, it is important to discuss fertility preservation options with TGD individuals, preferably before initiating any treatment, similar to how it is offered to patients whose reproductive system may be affected for instance by chemotherapy [7,8].
Reproductive rights are among the fundamental human rights granted by international and Spanish law. Various clinical guidelines, such as those by the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) [9], the Endocrine Society [10], and the American Society of Reproductive Medicine [11], recommend informing individuals about reproductive options before starting hormonal or surgical treatment [12,13]. The growing awareness and interest in transgender issues in recent years has spurred an increasing number of investigations in this field. One area of focus is the desire of TGD individuals to preserve fertility and have children [5,14-19]. However, in Spain there is a lack of data available on this topic. Existing literature exploring the utilization of assisted reproduction techniques in the TGD population reveals low usage rates and various barriers, including restrictive legislation in some countries, the cost of fertility preservation, psychological challenges during gamete collection, difficulties with ovarian stimulation, and underestimation of the importance of preserving future fertility, particularly in TGD adolescents. Social acceptance and local legislation concerning the rights of TGD families also influence choices and interest in fertility preservation [20]. Data differ considerably among countries, as was evidenced in a recent systematic review by Stolk et al. [5] that included 79 studies from 16 countries. The purpose of our study was to investigate reproductive desire and fertility preservation among TGD individuals attending a gender identity reference unit in Spain.
Methods
We conducted a unicentric questionnaire-based cross-sectional study among TGD individuals. Our unit has served as a reference center for the TGD population since 2007, conducting an average of 200-225 initial consultations per year. Our multidisciplinary team comprises specialists in psycho-sexology, pediatrics, endocrinology, general surgery, plastic surgery, gynecology, assisted reproduction and phoniatrics.
In Spain and the Valencian Community, the Public Health System covers a wide range of procedures, including assisted reproduction. Each case is assessed individually according to public funding criteria, which apply to TGD individuals on the same basis as to other populations with fertility problems. Fertility preservation (FP) is free and is offered to all eligible TGD patients at the initial assessment by the endocrinologist, who provides a detailed, individualized verbal explanation of the steps required for gamete collection. All TM up to the age of 40 and TW up to the age of 55 who do not have children are considered eligible for FP. Interested people are further counseled by hospital gynecologists with expertise in the field and referred to the Assisted Reproduction Unit at a tertiary hospital in the same city if in vitro fertilization is required. TW are offered masturbation-induced sperm retrieval and cryopreservation, while TM are offered ovarian stimulation followed by ovarian puncture and oocyte cryopreservation. Patients are advised to undergo the gamete collection prior to GAHT initiation in order to avoid unnecessary treatment interruption or gamete deterioration. However, they are informed that gamete collection can be performed at any time, even after GAHT initiation, if the gonads are preserved. To this end, they are advised to discontinue testosterone treatment for at least 3 months, in the case of TM, until adequate testosterone levels are achieved; and to discontinue estrogens and antiandrogens, in the case of TW, until a good quality sperm sample is obtained.
The questionnaire was voluntary and anonymous, administered on paper prior to a regular medical visit at the endocrinology department. Data collection took place between January 2019 and March 2020. Participants under 15 years of age were excluded from the study, while those between 15 and 18 years of age were included only with written consent from their parents. Before the survey, we ensured that each patient received individual information and advice regarding available fertility preservation options, long-term reproductive solutions, and the deadlines and procedures necessary for gamete collection. All participants signed an informed consent form for the study, which was approved by the hospital’s Ethics Committee.
The questionnaire consisted of 12 single and multiple-response questions. The first section gathered socio-demographic data, including age, gender, sexual orientation, civil status, and whether participants already had children. The next section contained questions regarding duration and types of treatment received up to the moment of completing the questionnaire. We also asked whether the potential loss of fertility could be a reason for delaying or interrupting of GAHT. The section focusing on reproductive desire consisted of 5 questions regarding the general desire to have children, including adoption and interest in assisted reproduction techniques.
Results
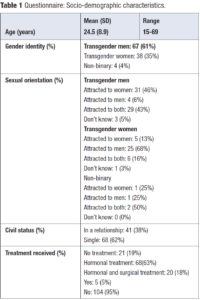
A total of 109 TGD individuals completed the questionnaire. The age range of participants was 15 to 69 years, with a mean age of 24.5 years. Among the respondents, 22% were under 18 years of age and 4% were over 45. Of the participants, 35% (n = 38) were identified as TW, 61% (n = 67) as TM, and 4 participants identified as NB. In terms of sexual orientation among TM, 46% (n = 31) were attracted to women, 6% (n = 4) to men, 43% (n = 29) were bisexual, and 3 individuals were unsure. Among TW, 68% (n = 26) were attracted to men, 13% (n = 5) to women, 16% (n = 6) were bisexual, and 1 individual was unsure. Among NB respondents, 2 were bisexual, 1 was attracted only to men, and 1 only to women. Regarding civil status, 62% did not have a stable relationship and 38% were in a relationship. Out of the 109 participants, 4.6% (n = 5) already had children at the time of participating in the survey.
Regarding the transition process, 19% had not started any therapy, 63% were on GAHT, and 18% had received both GAHT and gender-affirming surgical treatment. The loss of reproductive capacity was not considered important enough to delay or stop treatment in 89% of participants (n = 97). Nine participants considered it a valid reason for delaying the transition process, although they would not interrupt the treatment they had already initiated. Only one respondent chose the option of stopping the treatment until having children, and one chose to delay it until gamete collection.
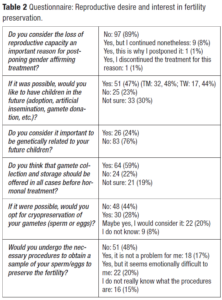
In terms of general reproductive desire, 47% of participants (n = 51) expressed a desire to have children in the future, 23% (n = 25) did not, and 30% (n = 33) were undecided. A similar percentage of TM (48%; n = 32) and TW (44%; n = 17) had reproductive desire. Twenty-four percent preferred to have genetically related children. Analyzing by age groups, among individuals aged 25 years and younger (n = 80), 46% (n = 37) desired children, 16% (n = 13) did not, and 38% (n = 30) were undecided. Among those older than 25 years (n = 29), 48% (n = 14) expressed a desire to have children, 42% (n = 12) did not, and 10% (n = 3) were undecided.
Regarding fertility preservation procedures, 59% believed that they should be offered to all TGD patients, 22% did not consider it necessary, and 19% had not previously reflected on the topic. In terms of personal choice, 28% (n = 30) of participants expressed an interest in fertility preservation, 20% (n = 22) would consider it if gamete preservation was offered, and 44% would refuse it. Only 17% of patients were convinced they would undergo all the necessary gamete collection procedures, 20% found it emotionally difficult, and 48% would not pursue it. The remaining participants (15%) felt that they had not been adequately informed on the topic. There was a significant difference between the interest and attitude of TM and TW toward fertility preservation techniques. If offered, 58% of TW and 24% of TM would choose to undergo these procedures, while 55% of TM and 24% of TW would refuse. A summary of the results can be found together with the complete questionnaire in Table 1 and Table 2.
Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study conducted to assess aspects of this topic in the Spanish TGD population. Similar research has been conducted in various countries across Europe, Asia, Australia, and North and South America [5,14-18,20]. However, comparing the results is challenging due to significant differences in methodology (questionnaires used) and socio-demographic characteristics of the studied populations, such as age, sex assigned at birth, inclusion of single-sex cohorts, previous treatment, and the prevalence of participants who have already had children before the study, which has been observed in some cohorts at a rate of 40% [16].
Although we excluded from our study patients under the age of 15 and those aged 15-18 who did not have parental consent to participate, we do not believe that this could have influenced the results or introduced bias. Nevertheless, it is important to note that voluntary participation as a data collection method can introduce a certain percentage of bias.
The peculiarity of our cohort is its young age, which means that many patients, like most of their same-aged peers, have not yet considered having children or been in a stable relationship.
We observed a low rate of surgical interventions, approximately 18%, which included various procedures ranging from mastectomy (which does not affect fertility) to oophorectomy with hysterectomy, phalloplasty, orchiectomy, and vaginoplasty. The surgical group was therefore heterogeneous, with mastectomy being the most common intervention, and comprised only 20 out of 109 patients (18%). In this context, it is difficult to analyze and compare the reproductive desire of those who underwent gonadectomy, which irreversibly impairs their fertility, and those who did not undergo surgery.
The desire to have children, whether genetically related or adoptive, was present in 47% of respondents, with similar levels among TM (48%) and TW (44%). These results differ slightly from previous studies where reproductive desire was present in 30-40% of participants assigned male at birth [16,20] and 54% of participants assigned female at birth [18,21]. In many studies, TM have shown a higher interest in having children compared to TW, even though the procedures required for oocyte collection are more complex and carry a higher risk of adverse effects [4,5].
In terms of acceptance of assisted reproduction techniques, the trend is reversed: the data reveal a higher acceptance among TW. In our study, 37% of all participants expressed willingness to undergo the procedures (58% of TW and 24% of TM), while 48% were certain they would refuse it (55% of TM and 24% of TW). This tendency may be explained by the greater complexity and stress associated with gamete collection in the case of individuals assigned female at birth [22,23].
Compared to previous studies, our cohort exhibited a low preference for having genetically related children (24% versus 33%), aligning with the prevailing trend in the literature favoring alternatives such as adoption [5,19,24].
Interestingly, when the data by age groups were analyzed, we observed that many individuals younger than 25 years of age had not yet reflected on the issue of their future fertility, as 38% of individuals in this age group were undecided. To prevent potential regret in the future, it is crucial to adequately inform and counsel patients about the potential impact of gender-affirming treatments on their fertility. Fertility preservation should be offered before initiating GAHT, and reproductive desire should be reassessed in a personalized manner before irreversible surgeries are performed [5,23].
Although a significant number of patients expressed a desire to have children in the future, most of them did not see it as a reason to postpone the initiation of treatment. In fact, an interesting finding in our study was that 89% (n = 97) stated that they would not delay treatment, which contrasts with previous studies where, for example, only 55% of participants in an Australian cohort responded similarly [24].
Another interesting finding in our study was the high percentage of bisexual individuals, particularly among TM (43%), which could potentially enable genetically related children in future relationship through cryopreservation of gametes. Among TW, 29% were attracted to women or both sexes, which would equally allow for future gestation using the patients’ sperm.
Regarding the information received on fertility preservation methods, 15% of participants in our center considered it insufficient, compared to 40% found in previous studies [24]. However, it is important to consider that our study design included discussing fertility preservation options with patients during the visit prior to completing the questionnaire. This information was given verbally, which may explain why some patients found it insufficient. A lesson learned from this data is that it would be useful to provide written information on the issues related to fertility preservation discussed during the first visit, which patients could read again outside the hospital.
The patients’ right to information is crucial, and healthcare professionals should make every effort to provide it as an inherent part of care within gender identity units. Recent studies present an encouraging outlook, particularly in research involving adolescents and young adults, as a significant proportion of patients received counseling before undergoing treatment [5,23]. Notably, our study revealed that even individuals who were undecided or lacked interest in having children, recognized the importance of receiving all the necessary information.
Conclusions
The findings of our study indicate that TGD individuals have an interest in having children in the future, even though they may not prioritize it when starting medical transition. This could be attributed to the young age of the participants of our study and a lack of information. Therefore, it is crucial for healthcare providers to prioritize informing and counseling patients about the procedures, enabling TGD individuals to reflect on the topic and understand the potential impact of gender-affirming treatments on their future reproductive capacity.