Introduction
Gender dysphoria in transgender people in many cases requires the initiation of safe and effective hormone treatment to develop the physical characteristics of their affirmed gender [1]. Transmasculine people (individuals who identify as men or on the masculine spectrum and were assigned female sex at birth, AFAB) initiate testosterone therapy to achieve the secondary characteristics of the affirmed gender and maintain sex hormone levels within the normal male range (called gender-affirming hormone therapy, GAHT). The long-term effects of these treatments on fertility are unknown, which is why the different scientific medical societies recommend advising on fertility preservation (FP) techniques ideally before starting GAHT [1-5]. In recent years, FP techniques have significantly increased in this population, probably because the reproductive wishes of transgender people have intensified, reaching at present up to 58% [6].
Oocyte and embryo cryopreservation are the established methods for FP, but these treatments have certain drawbacks, especially if GAHT has already started. The ongoing controversy revolves around the necessity to temporarily halt hormonal treatment and initiate an ovarian stimulation process. This process results in elevated estrogen levels, potentially causing undesired physical changes and triggering gender dysphoria [7]. We present a case of FP in a transgender young adult (TAYAs, transgender adolescents, and young adults) with GAHT established with some peculiarities.
Case report
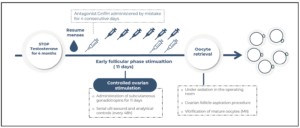
A 23-year-old AFAB transgender person, on testosterone therapy for gender affirmation for more than five years, presented for oocyte cryopreservation. Informed consent was obtained from him for the publication of this case report. His past medical history was significant for a bilateral mastectomy performed three years ago. His only medication was once every three months intramuscular testosterone undecanoate (Reandron® 1g/4 mL, Grünenthal Pharma Spain) since January 2018, achieving testosterone levels of 435 ng/dL in his last endocrinological control. After exposing the options, he stopped testosterone therapy, reassuming menses three months later, that is, 6 months after the last injection. The ovarian stimulation began 4 months after testosterone discontinuation, altogether, 7 months after the last injection of testosterone undecanoate. Transvaginal ultrasound evaluation was undertaken throughout the study and during the ovarian-controlled hyperstimulation (he was able to tolerate the transvaginal probe). Baseline transvaginal ultrasound demonstrated a normal uterus and ovaries, with an antral follicle count (AFC) of 21 follicles.
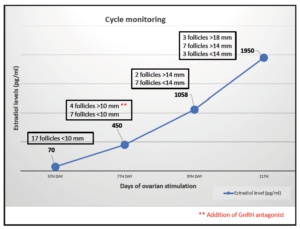
The initial values of anti-Mullerian (AMH) were 3.2 ng/mL with testosterone treatment. After discontinuation, four months later, a re-evaluation was conducted, revealing an AMH value of 2.9 ng/mL. Testosterone levels decreased to the range of cisgender women of reproductive age (40 ng/dL). In the early follicular phase, a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist protocol was started with follitropin alfa subcutaneous (150 IU daily, Gonal-f; Merck Serono Europe, London). By mistake, he started treatment with cetrorelix (Cetrotide; EMD Serono, Canada) instead of follitropin alfa, causing more pronounced follicular arrest. Four days after the initiation of cetrorelix, this medication was discontinued and follitropin was started at established doses. He restarted the GnRH antagonist again on the 7th day of stimulation, at which point the estradiol serum level was measured at 450 pg/mL (Figure 1, follicular growth and hormone levels cycle monitoring). Due to standard ovarian response to stimulation with multiple follicles measuring >17 mm average diameter, an HCG trigger (Ovitrelle 250 mic, Merck Europe, Amsterdam) was prescribed at 8 PM on the 11th day of stimulation. Transvaginal egg retrieval occurred 36 hours after the HCG injection (Figure 2). A transvaginal ultrasound-guided oocyte retrieval was undertaken under conscious sedation and 12 cumulous oocyte complexes were retrieved. Ten mature oocytes were cryopreserved through vitrification. No ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome was observed. After the procedure, he restarted testosterone therapy.
Discussion
In recent years, the transgender population has improved their health care in all aspects, and one of them is reproductive care. According to the recommendations of multiple organizations like WPATH or ASRM [2,8]. FP counselling before gender-affirming treatments, including hormone therapy, should be performed [1,5,9]. Regarding FP procedures, several case series have been published in recent years, being currently a highly debated topic. Before starting GAHT, oocyte vitrification results are comparable to those of the cisgender female population of the same age, similar levels of ovarian reserve markers, and an equal number of retrieved oocytes after ovarian hyperstimulation, even in transgender adolescents [10-13]. However, doubts exist in transgender people after they have initiated GAHT, since the long-term effect of testosterone on the follicular population in the ovary is unknown [14]. The cessation of GAHT before starting oocyte preservation has been established, although the period necessary to initiate the cycle is unclear [15]. Approximately three months has been agreed, based on the recruitment period of the follicles from the primordial to the antral stage, sensitive to the gonadotropin action (approximately 70 days), and due to a potential teratogenic effect of testosterone, like methotrexate, requiring a washout period of minimum three months [16,17].
Our case is in line with the published series, highlighting the start of GAHT at a young age, at 17 years, and given for more than 5 years without any cessation. The cessation of testosterone was agreed upon, and a good response to controlled ovarian hyperstimulation was observed, obtaining 10 vitrified mature oocytes. However, there are few reports of transgender and non-binary adolescents and young adults (TAYAS) on testosterone therapy, but the published data appear to be reassuring [18]. Some reported cases show similar AMH values and AFC after stopping testosterone when compared with those obtained in cycles of cisgender women of the same age and find no differences in the doses of gonadotropins administered or in the obtained number of oocytes nor mature oocytes [19-21].
There is some data regarding the effect of testosterone on follicle growth and the oocyte quality. In in vitro murine studies, follicular development was affected, and the oocyte meiotic competence was impaired when testosterone levels were high [22]. In addition, in a mouse model mimicking testosterone therapy given to transgender people, ovarian stromal aberrations have been observed, and data about follicular development have been obtained [23,24]. Assisted reproduction techniques (ART) in this murine model showed worse reproductive outcomes, including significantly impaired fertilization in oocytes retrieved from animals on active testosterone treatment and lower implantation and live birth rates [25]. Despite this, there are case reports documenting ovarian stimulation in transmasculine individuals who maintained gender-affirming testosterone therapy throughout the stimulation process. These cases are characterized by extended stimulation cycles and the requirement of high doses of gonadotropins. Despite these challenges, a notable number of matured oocytes were retrieved, ranging from 9 to 25 in the five reported cases [26-30]. Additionally, among these seven cases undergoing ART while continuing testosterone therapy, two individuals achieved euploid blastocysts. These blastocysts were subsequently transferred to their cisgender female partners, resulting in two live births without neonatal complications. It is worth noting that both studies emphasized anomalies in early embryogenesis, including a low blastulation rate and a high percentage of aneuploidies [26,30].
There is currently no information on the potential effect of high doses of testosterone on the epigenetic aspects of newborns or their long-term health, so it is essential to continue studying these hormonal effects and given the data, discontinue testosterone before performing FP techniques.
Conclusions
It is imperative to provide good FP counselling before initiating GAHT and explain the available FP options. Stoppin testosterone therapy before starting the oocyte vitrification procedure has been shown to be safe and efficient, although it is not free of drawbacks, such as the resumption of menses causing important dysphoria. Although some studies show good reproductive results without stopping testosterone therapy, more studies are required regarding elevated testosterone levels and its impact on embryonic development, aneuploidy, and the long-term health of offspring.
Author Contributions
AB—detailed data collection and careful writing of the manuscript. AB—literature review and manuscript writing. GC—literature review and manuscript writing. MM— clinical management and review of the scientific research. DM—clinical management and review of the scientific research.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The authors obtained the approval of our local ethics committee from Hospital Clínic de Barcelona (Reg HCB/2021/0250). Informed consent was obtained from the patient included in this case report.
Acknowledgment
Thanks to Dolors Manau for pushing me to keep writing and sharing knowledge.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.